
The third comprehensive scientific survey of Xinjiang major national scientific and technological projects is underway. At present, all 29 projects have been launched and have entered a critical period of field investigation.
Lake Aiding is the lowest land point in my country, and its lake surface is more than 150 meters lower than sea level. The scientific expedition team members from the Chinese Academy of Sciences conducted sampling of microorganisms here, which is also one of the important contents of the third comprehensive scientific investigation in Xinjiang.

Member of the Third Xinjiang Comprehensive Scientific Expedition Team Associate Researcher at the Institute of Xinjiang Ecology and Geography, Chinese Academy of Sciences Fang Baozhu: In the first two Xinjiang scientific expeditions, there was almost no microbial resources. Through this scientific investigation, we can understand the microbial community structure in the entire salt lake bottom mud, and use this microbial ability to resist stress and promote growth, and make it into biological bacteria fertilizer to promote the growth of plants in saline-alkali land.
The third comprehensive scientific survey in Xinjiang is a major scientific and technological project deployed by the state. It was launched at the end of 2021. It is organized by the Ministry of Science and Technology and the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and participated by hundreds of domestic universities and research institutes. It is divided into five areas, namely the Tarim River Basin, the Ili River Basin, the Ertzis River Basin, the Tianshan North Slope Economic Belt and the Turpan Hami Basin, conducts five major aspects: water resources, land agriculture, biology, mineral energy and ecological environment, aiming to comprehensively understand the resource and environment foundation of Xinjiang, scientifically evaluate Xinjiang's resource and environmental carrying capacity, and propose Xinjiang's future ecological construction, green development strategy and roadmap.

Deputy Director of the Office of the Third Xinjiang Comprehensive Scientific Expedition Working Group and Director of the Research Department of the Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography, Chinese Academy of Sciences Zhou Xiaobing: The implementation period of the third Xinjiang scientific expedition is from 2021 to 2025, and the project has been implemented to the mid-term. This year, nearly 100 teams are expected to conduct resource surveys in various aspects in Xinjiang. This time is not only a critical period for our field surveys, but also an important critical period for our results output and summary.
Scientific Expo continues to be promoted, and a number of important results have been achieved
Since it was launched at the end of 2021, the third comprehensive scientific inspection in Xinjiang has been steadily advanced and a number of important results have been achieved. In terms of water resources, through field investigations, the scientific expedition team members initially identified the water volume of multiple rivers in some unmanned areas and unmonitored data areas, and discovered new available water resources.
Deputy leader of the Third Xinjiang Comprehensive Scientific Expedition Working Group, Director of the Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Through this scientific expedition, we re-analysed some unmanned areas (no information) and low data coverage areas, and found that due to the lack of data at that time, the water resources and precipitation in some areas were underestimated. For example, in some mountains on the northern slope of Kunlun Mountain, the precipitation was underestimated by about 20% to 40%.
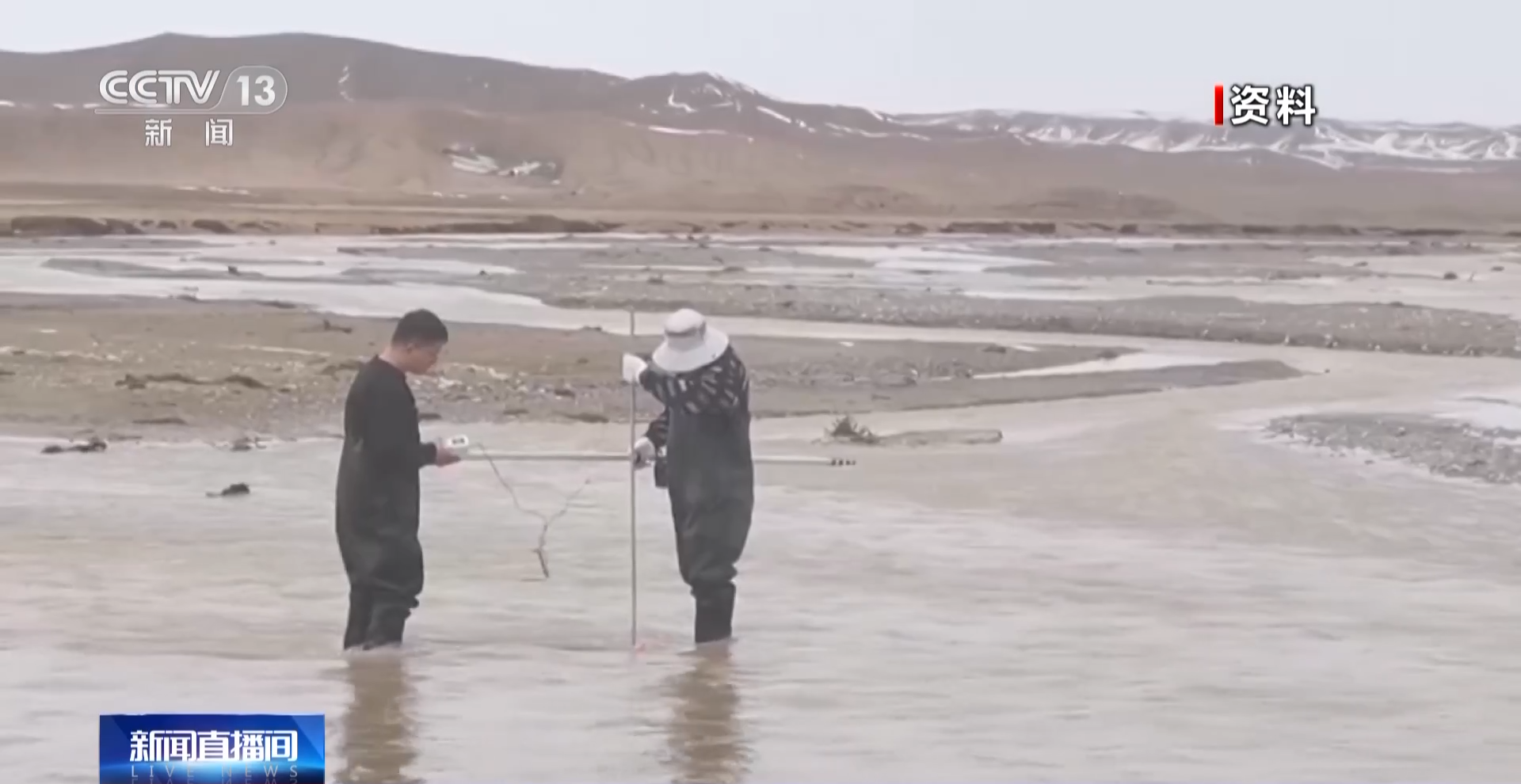

Scientific Expedition Team members found that in the past 20 years, the land water reserves on the northern slope of Kunlun Mountain have been the area with the most significant increase in the entire northwest arid area, and the area, number of mountain lakes and the runoff of major rivers have increased significantly. For example, the average annual runoff of the Hotan River and the Cherchen River in the past 10 years increased by 22.15% and 50.17% compared with the multi-year average (1957— 2021) respectively; the area of Ayakkumu Lake and Akikkule Lake increased by 68.53% and 58.22% respectively from 1990 to 2021. The increase in water resources on the northern slope of Kunlun Mountain will provide better support for the green and high-quality development of the region and the consolidation of water security achievements in poverty alleviation.

Deputy leader of the Third Xinjiang Comprehensive Scientific Expedition Working Group, Director of the Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography, Chinese Academy of Sciences Zhang Yuanming: These water volumes have not been estimated before, so on this basis, we will play a very important supporting role in the development of water resources in some potential development zones in the future.
Biodiversity Survey Discovers New species of animals and plants
In terms of biological resources and biodiversity, based on understanding the background, the scientific research team also discovered some new species or new recorded species in China, which not only enriched the understanding of Xinjiang's biodiversity, but also further revealed environmental and climate change and provided a scientific basis for ecological protection and resource development and utilization.
The third comprehensive scientific investigation in Xinjiang carried out a systematic biodiversity survey and assessment work, and the survey areas involved important ecosystems such as oasis, Gobi, desert, salt desert, salt lake, swamp wetlands, grasslands, mountain coniferous forests. In the Ertzis River Basin, the scientific expedition team discovered a new species of endemic hook shrimp. By comparing and analyzing the genetic and distribution data of 3,180 hook shrimps around the world, it was proved that the Tianshan Mountains and its surrounding areas are one of the origins of cold-water organisms in the world.
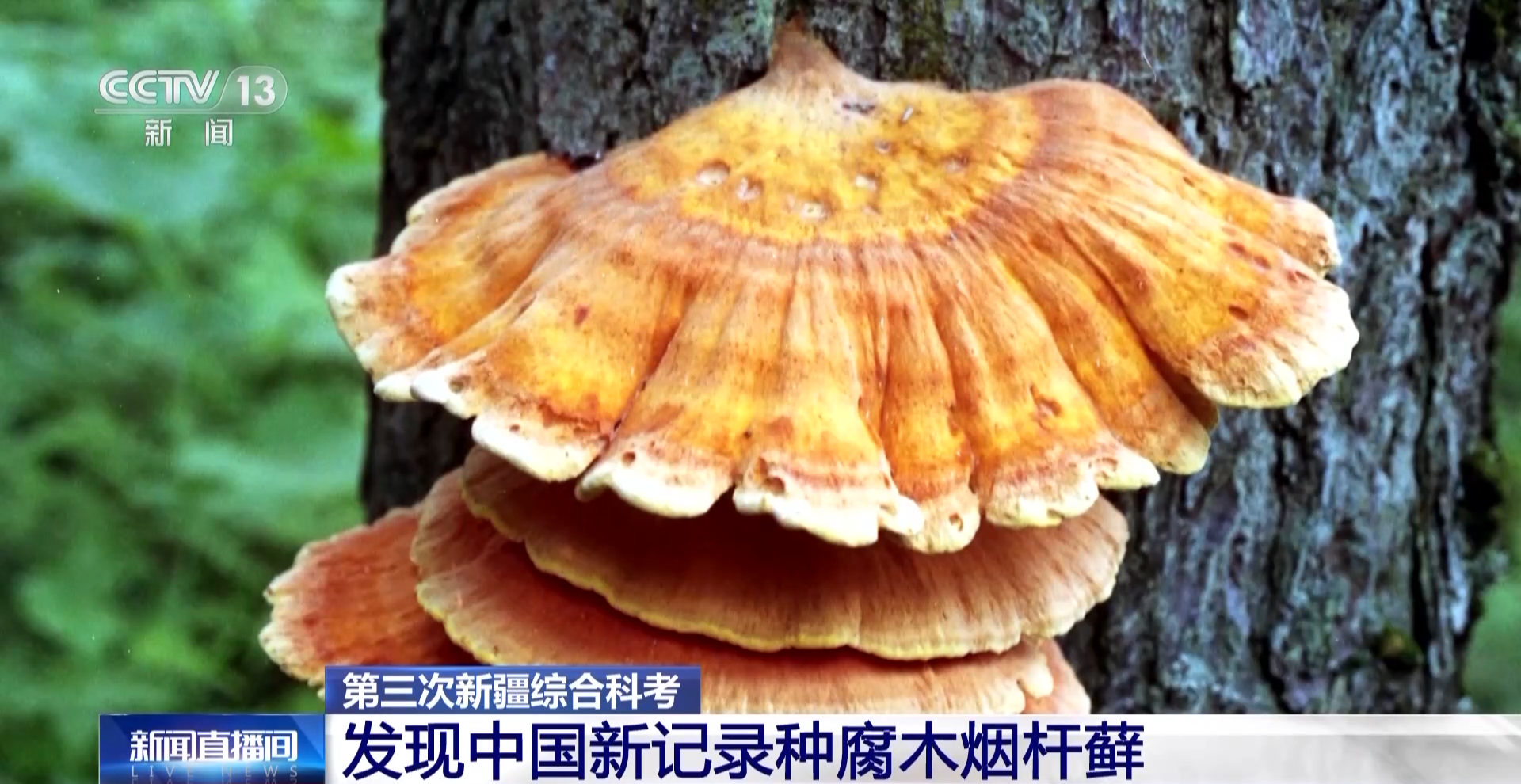

In the Tianshan wild fruit forest area, the scientific expedition team discovered a new Chinese record species of moss plant, 39 new Chinese record species of parasitic natural enemy insects, and a unique sulfate bacteria in Xinjiang. During the visit, the researchers showed the newly discovered rotten wood tobacco moss to reporters, which is a very rare bryophyte. Although it has distribution records in many countries, its population is small and it is included in the red list.

Member of the Third Xinjiang Comprehensive Scientific Expedition Team, Associate Researcher at the Institute of Xinjiang Ecology and Geography, Chinese Academy of Sciences Gao Bei: Rotten Wood Smoke-rod moss, which grows on rotten wood in ancient woodlands, is a new (record) moss species discovered in China. The moss species is the earliest branch of land plants. It is of great significance to us to have a deeper understanding of the evolution of moss (and land plants). Xinjiang, especially the Tianshan wild fruit forest area, biodiversity is an area that is worth exploring. With the continuous advancement of the third Xinjiang scientific expedition, we may bring more new discoveries..
New scientific and technological means help “sky and earth integration” monitoring
In the third comprehensive scientific investigation in Xinjiang, the application of a variety of new scientific and technological means is a highlight. Ground observation stations, drones, satellites and other equipment cooperate with each other, making large-scale field surveys more efficiently and scientific research data more accurate, comprehensive and rich.
In the desert areas of the Turpan Basin, the scientific expedition team members set up an automatic meteorological station, which can achieve "sky-ground integration" monitoring with a series of scientific and technological means such as aerial drones.
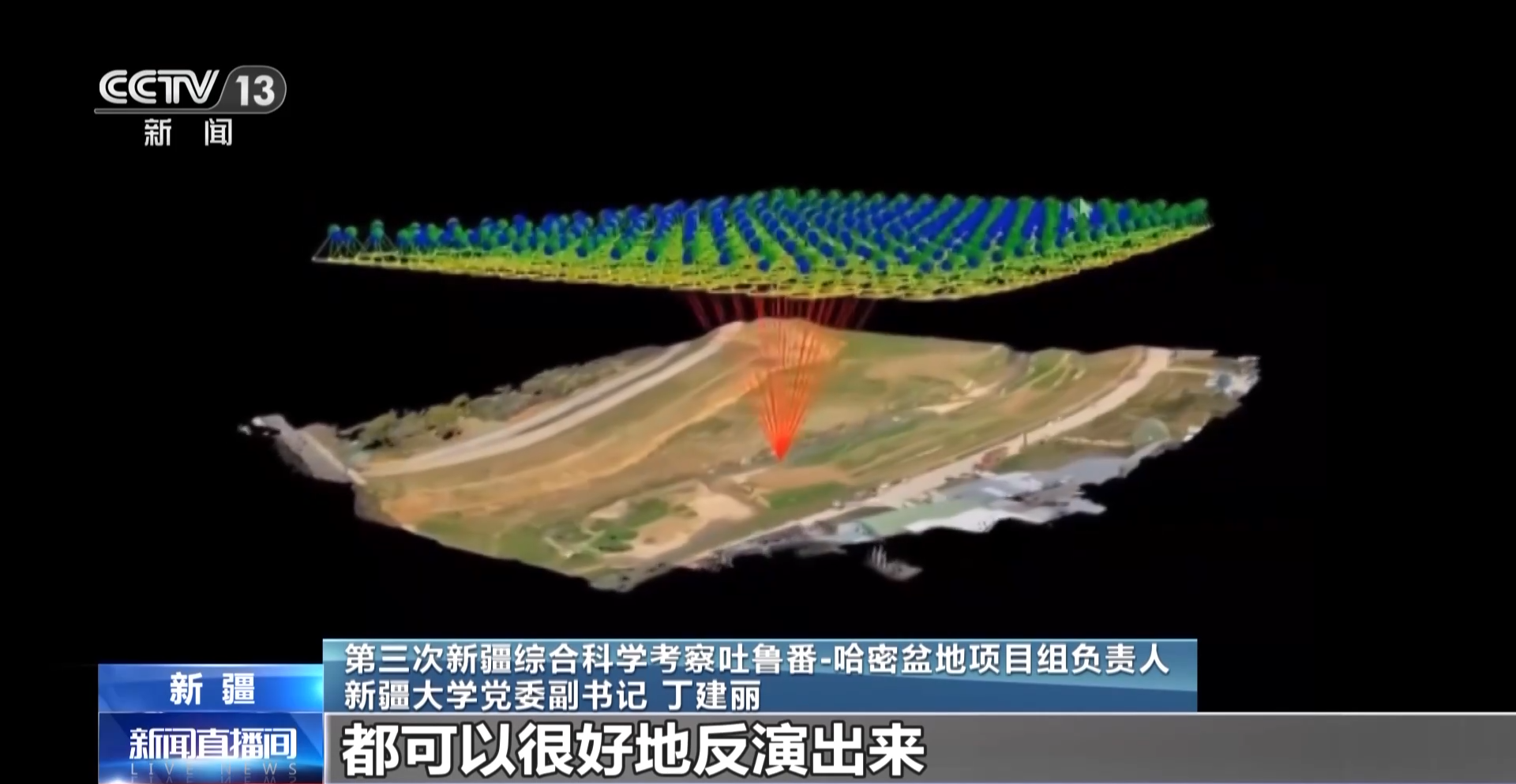
Held of the project team of the third Xinjiang comprehensive scientific expedition Turpan-Hami Basin, Deputy Secretary of the Party Committee of Xinjiang University: In such a large area, due to the few observation stations, a large amount of data is missing. Drones can play a larger-scale data acquisition. Through the drone's platform, the soil density, texture and structure in the entire field of view can be clearly seen. Through digital hydrological technology, we can invert the naturally formed sections of the river and the corresponding water volume, including the 3D terrain, well.

By integrating drone, satellite and Internet of Things technologies, the third Xinjiang Comprehensive Scientific Survey has built 26 new automatic monitoring sites for unmanned zone ecosystems, supplementing and improving the resource and environmental monitoring network of unmanned zones; the real-time collection app for field scientific expedition data is launched online, and at the same time, the first and second Xinjiang comprehensive scientific expedition databases have been rebuilt, a scientific expedition big data platform has been established, and the sharing services of Xinjiang scientific expedition data has been initially realized.

Deputy leader of the Third Xinjiang Comprehensive Scientific Expedition Working Group and Secretary of the Party Group of the Xinjiang Branch of the Chinese Academy of Sciences Chen Xi: Integrating the data of the first two scientific expeditions with the data of the third scientific expedition provides a scientific basis for us to find out the changes in the natural ecological environment in Xinjiang over the past 30 years; providing a technological roadmap for how Xinjiang will develop in 10, 20 and 30 years, how to make good use of natural resources and protect the ecological environment in the future, and also provides a very solid scientific foundation for our Xinjiang to better integrate into the national construction of the Belt and Road and the construction of the core area of the Silk Road Economic Belt.

